Patent
“Protect your inventions”
What is Patent?
Benefits of Patent Registration
At Spark Intellectual Property Services, we provide a complete range of patent registration, protection and enforcement services that are customized to your needs and specifications. They include the following:
Regional, National and International Patent Applications
Regional applications
This has effect in a range of countries, without having to file in all countries, following a single application process. Advantage also includes reduced costs and complexity. The EPO, ARIPO and OAPI are examples of PCT contracting states for which a regional patent can be obtained via the PCT.
National applications
This is filed directly at a national patent office or from a regional or international application under the PCT, once it enters the national phase. The UK Patent Office is an example.
International applications
This is a centralized application which later can lead to the grant in any of the state contracting to the PCT which is operated by the WIPO. Advantage includes a single step where a wide range of countries is retained and formalities such as naming applicants and inventors and filing certified copies of priority documents can be done centrally.
Types of Applications
Each patent office utilizes different types of application and within each group comprised of specific types, such as utility patents, design patents and plant patents that vary in terms of substance and procedures.
Standard application
This is referred to as a non-provisional application and depending on the examination outcome; this may or may not result in the grant of a patent. This comprises all the necessary parts such as written description of the claims and invention.
Provisional application
This places an application on file to obtain a filing date and secure a priority date, but without the expense and complexity of a standard application. However, no enforceable rights can be obtained solely through the filing of a provisional application.
Continuation application
When the priority year has expired and further refinement or improvement is needed with a previous application, this type is being utilized to include other materials for enhancement. A “continuation-in-part” is possible for which the applicant may add subject matter undisclosed with the parent application but repeats substantial portion of the parent's specification, and shares at least one inventor with the parent application.
Divisional application
This can only contain subject matter in the application from which it is divided (its parent), but the filing and priority date is retained from the parent. This is useful if a unity of invention objection is issued because a patent can only claim a single invention.
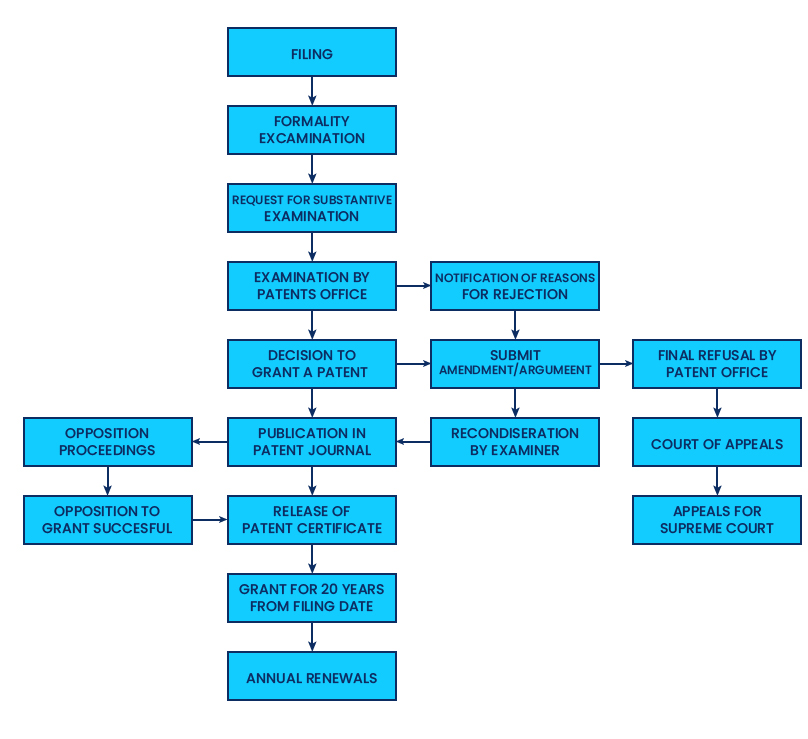
Standard Patent Flowchart